之前參與讀書會整理的筆記,雖然已經是 10 多年前的書了,印象中書裡介紹的 gcc, glibc 偏舊,與現版本實際測試發現的行為有些差異,不過並不影響觀念的釐清,推薦給想要深入了解 binary 建置流程,以及 executable/library 運行原理的朋友。
本文所有圖片和程式碼都來自原書內容。
Behind Building A Simple “Hello, World” Application
[hello.c]
1 |
|
可以直接使用 gcc 最簡單的格式編譯 hello.c。
1 | gcc hello.c |
上述過程可以分解為 4 個步驟: Preprocess, Compile, Assemble, Link,如下圖。
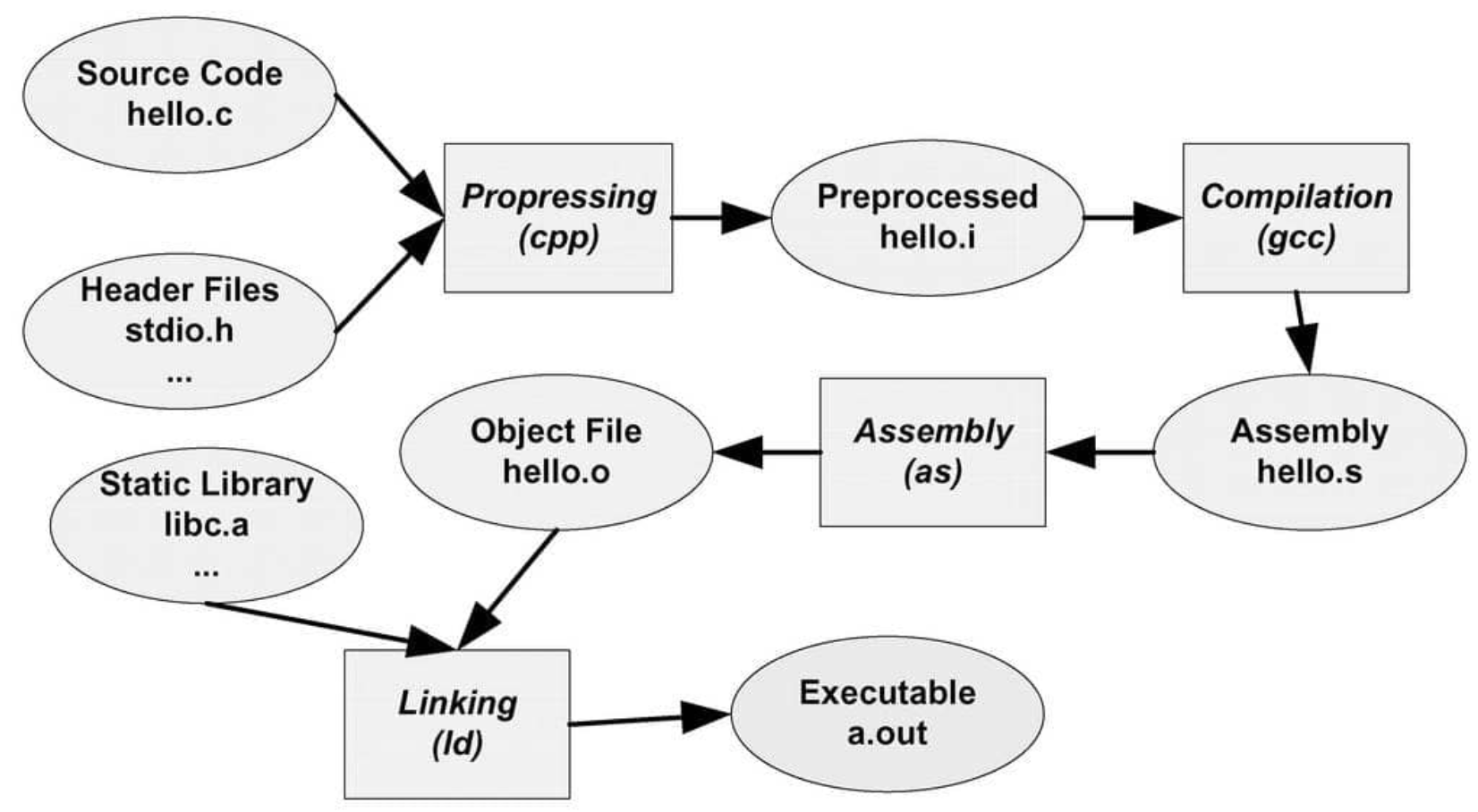
1 | gcc --save-temps hello.c |
Preprocess
進行以下處理
- 展開
#define - 處理 preprocessor directive (
#if,#ifdef, etc.) - 遞迴處理
#include - 刪除 comment
- 加上行號, 檔名標誌如
#3 "hello.c"(document) - 保留部分
#pragma給 compiler
- 展開
使用 gcc 只進行 preprocess:
1
gcc –E hello.c –o hello.i
1
cpp hello.c > hello.i
Compile
build 的核心,將 preprocessed 文件進行:詞法分析、語法分析、語義分析及優化後產生相應的 Assembly code 文件,後續小節會再做介紹。
使用 gcc 只進行 compile:
1
gcc –S hello.i –o hello.s
同時進行 preprocess 和 compilde:
1
/usr/lib/gcc/x86_64-linux-gnu/9/cc1 -I /usr/include/x86_64-linux-gnu hello.c
1
gcc –S hello.c –o hello.s
gcc 命令實際上是一系列編譯工具的封裝,它會根據參數去調用 cc1 (cc1plus), as, ld。
Assemble
- 將 Assembly code 轉為 machine code,相對 compiler 較為簡單。可利用 as 來進行:
1
as hello.s -o hello.o
1
gcc –c hello.s –o hello.o
- 或利用 gcc 直接進行 preprocess, compile 和 assemble:
1
gcc –c hello.c –o hello.o
Link
根據剛剛產生的 object file,使用 ld 來產生一個能正常運行的 HelloWorld program (以下指令省略路徑):
1
ld -static crt1.o crti.o crtbeginT.o hello.o -start-group -lgcc -gcc_eh -lc-end-group crtend.o crtn.o
(在接下來的章節中會進一步再做介紹)
What Does Compiler Do?
以下對 Compile 的流程做更詳細的介紹,一般可以分為以下步驟:
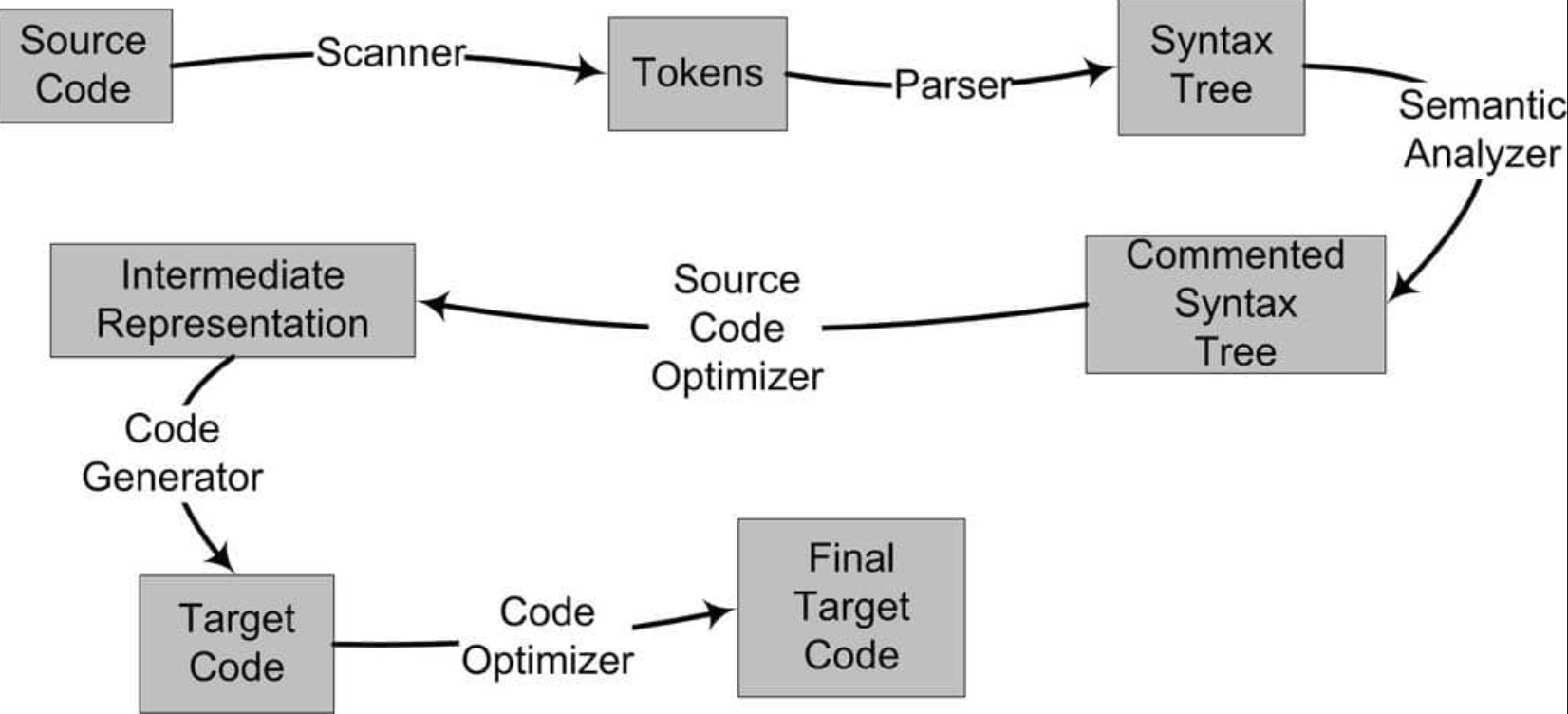
以下用一行簡單的 assignment statement 為例,解釋各個階段的過程:
1 | array[index] = (index + 4) * (2 + 6) |
Lexical Analysis
Scanner - 輸入 source code,將其分割輸出成一系列的 token,如上面那行 code 有 16 個 token,table 如下:
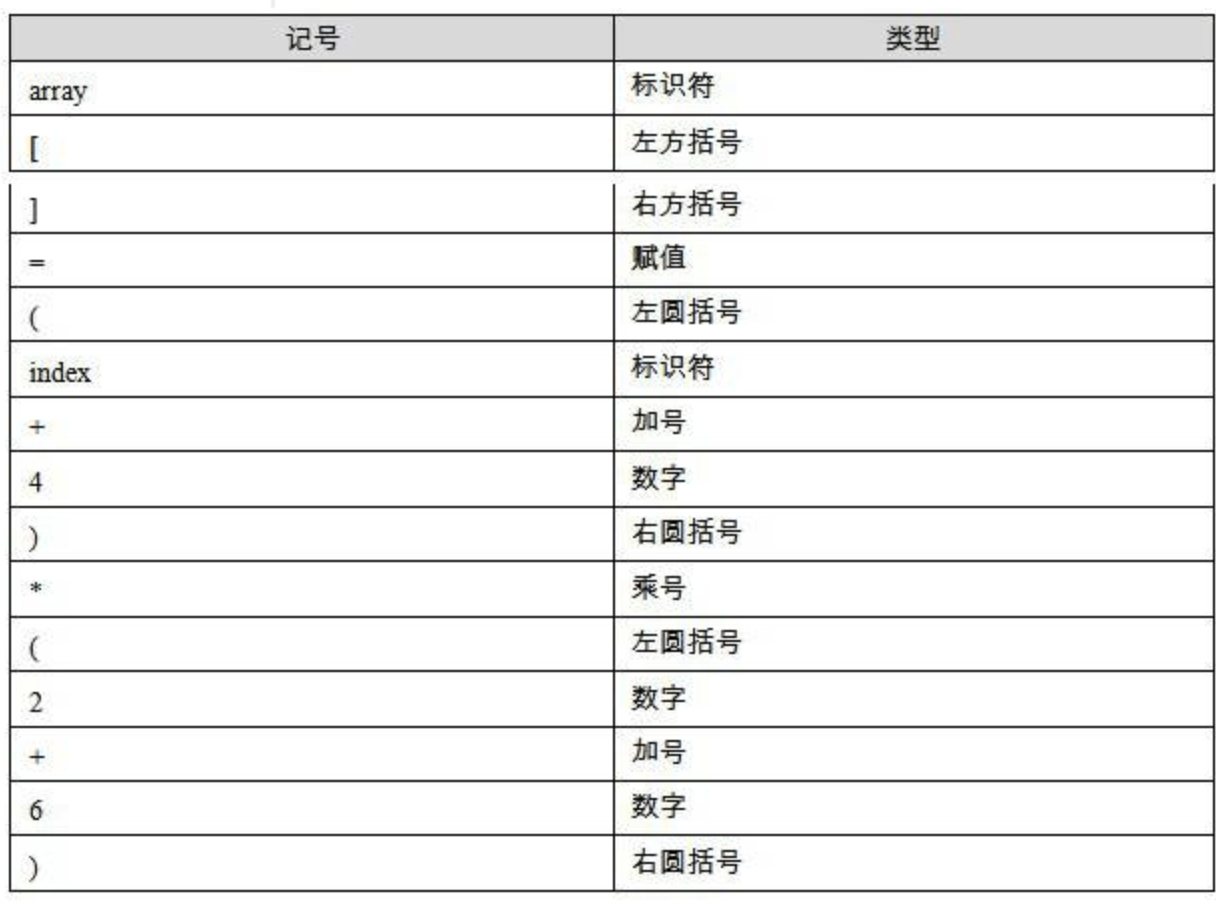
採用類似有限狀態機(finite state machine) 的算法。
可以利用 lex/flex 等工具,描述 token 的 regular expression 來實現 scanner。
Syntax Analysis
Grammer parser - 將 scanner 產生的 tokens 進行句法分析產生以表達式(Expression) 為 node 的 Syntax tree 如下:
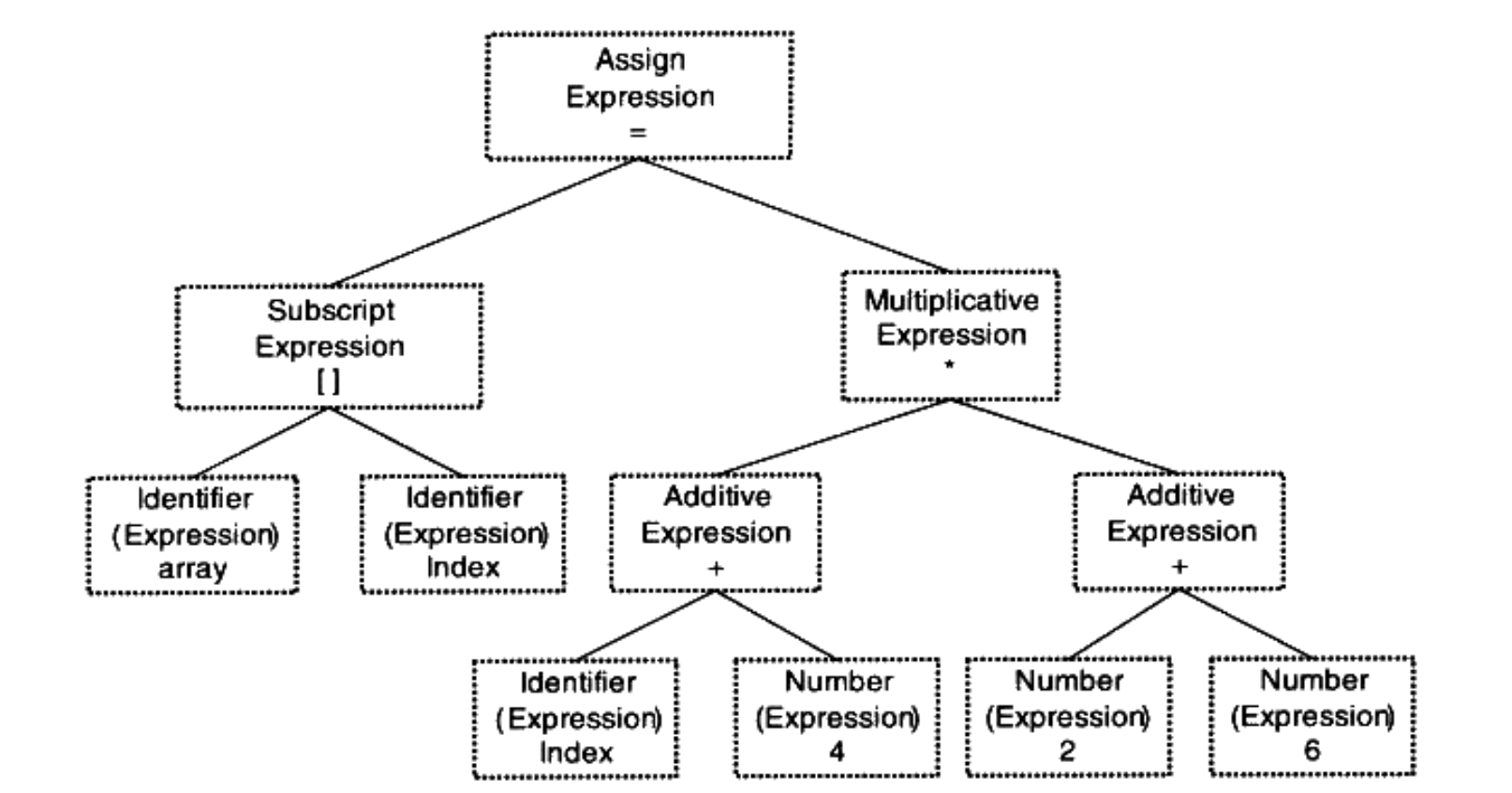
分析過程採用 Context-free Grammer。
operator 優先度(括號>乘除>加減)、表達式不合法(括號不匹配、缺少 operator/operand),都在這個階段處理。
可以利用 yacc/bison 等工具,給定句法規則來實現解析,進而構建出 syntax tree。
Semantic Analysis
Semantic analyzer - 進一步檢查語句是否有真正的意義。
Static semantic - 如型別的匹配、轉換,是在 compile time 就能檢查的,如
- float assign to pointer: 不匹配
- float to integer: 需要隱式轉型
Dynamic semantic - 只有在 runtime 才能確定
- 0 作為除數
經過這個階段,syntax tree 的每個 node 會被標誌類型,和加上隱式轉換的 node,如下:
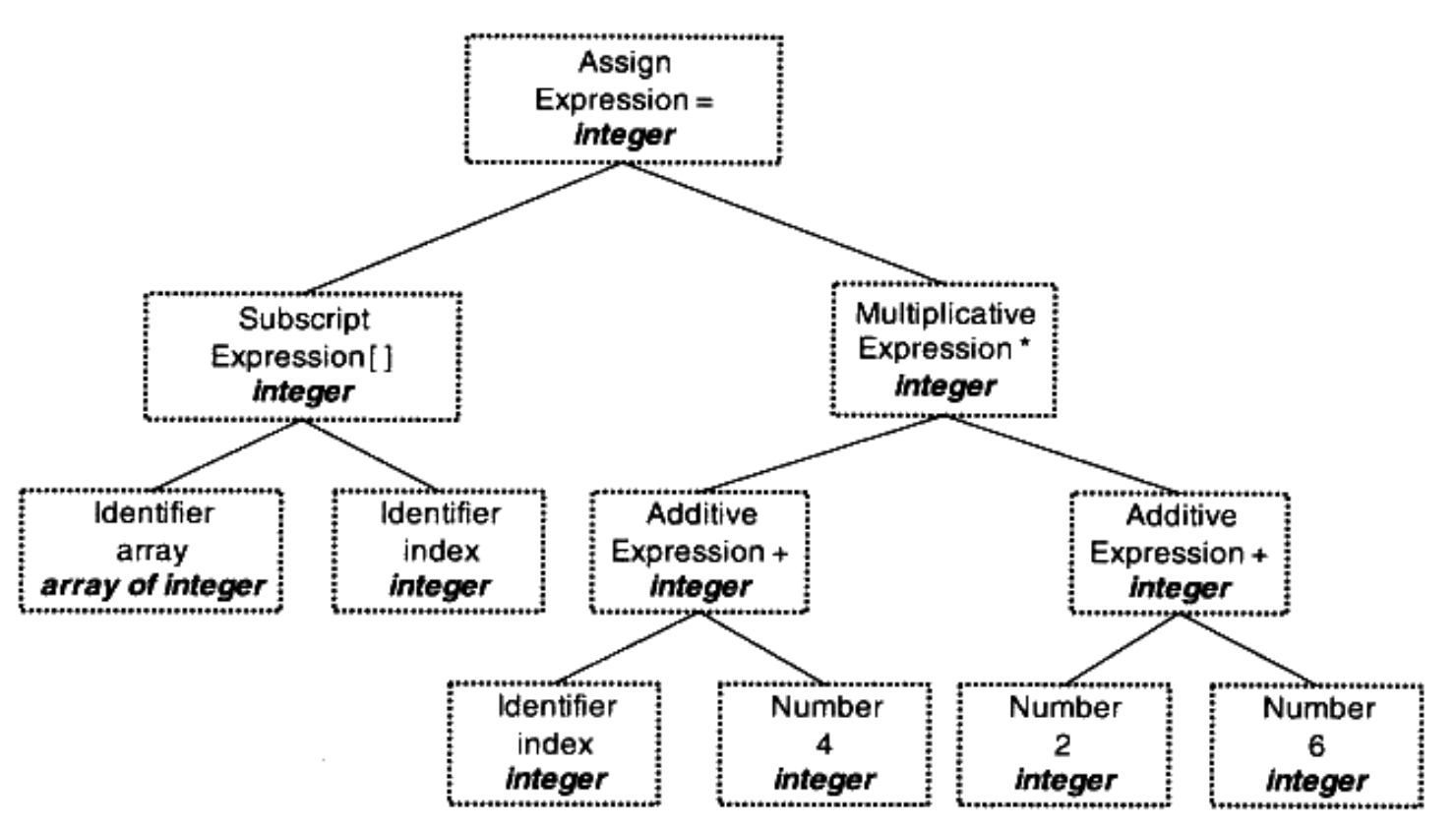
Intermediate Code Generation and Optimization
Source code optimizer - 優化 source code,在不同的 compiler 有不同的定義和優化方式,簡單的例子如將上述的 expression
(2+6)明顯能做簡化,如下圖: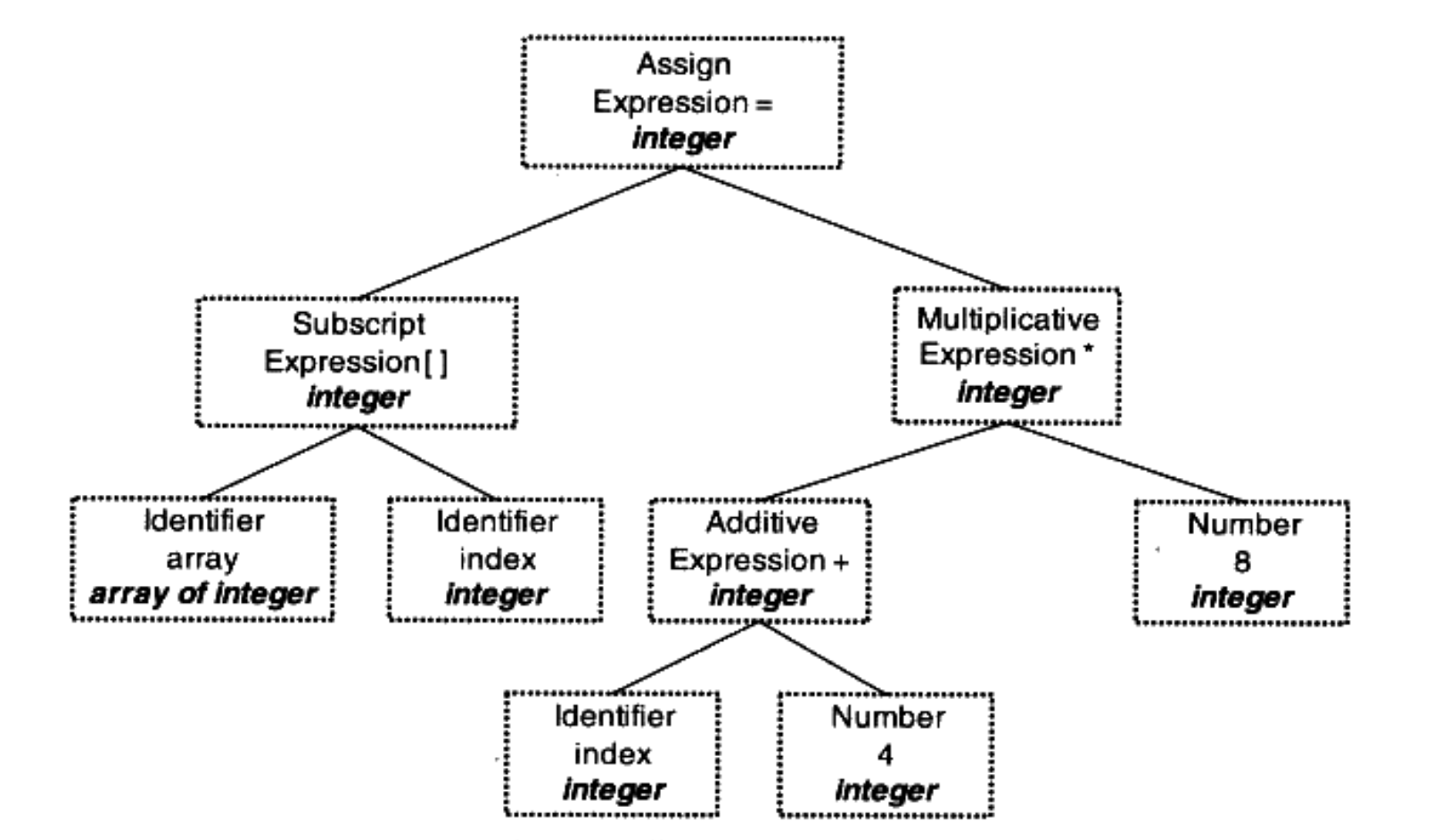
Intermediate code generation - 直接優化 Syntax tree 比較困難,常見的方式會先根據 tree 產生 intermediate code 在進行優化,常見的形式有 Three-address Code, P-code,前者最基本的形式如下:
1
x = y op z
尚未優化的 Syntax tree 翻譯成 Three-address Code 如下:
1
2
3
4t1 = 2 + 6
t2 = index + 4
t3 = t2 * t1
array[index] = t3結合 Optimizer 能先將
2+6的結果計算出來,再加上變數重複利用,使得上述 code 能優化如下:1
2
3t2 = index + 4
t2 = t2 * 8
array[index] = t2Intermediate representation 使得 compiling 的過程可以被分為 front-end, backend,前者負責 source code 到 IR,後者負責 IR 到 target machine code,利於跨平台的編譯。
Target Code Generation and Optimization
- Code generator - IR code 轉換為 target machine code (依賴 platform)。上面例子的 IR code 轉換為 x86 的 assembly language 可能為如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8movl index, %ecx ; value of index to ecx
addl 4, %ecx ; ecx = ecx + 4
mull8, %ecx ; ecx = ecx * 8
movl index, %eax ; value of index to eax
movl %ecx, array(,eax,4) ; array[index] = ecx
disp(base, index, scale)
[base + index*scale + disp] - Target code optimizer - 進行優化,如刪除多於指令、位移代替乘法運算等,以上述 code 來說,能用較複雜的 Base Index Scale Addressing 的 lea 指令來取代乘法和加法,優化如下:
1
2
3movl index, %edx
leal 32(,%edx,8), %eax
movl %eax, array(,%edx,4) - index, array 地址還沒有確定,如果這兩個變數和上面的 source code 在相同的 compile unit,那 compiler 可以處理,但如果不在的話就需要在 link 階段做。
Introduction of “Linking”
程序切割不同 module,易於閱讀、重用、開發、測試。
module 間需要 call function、access variable,引伸出 symbol 的概念,有些 module 定義 symbol、有些引用 symbol,link 的過程類似於拼拼圖。
過程主要包含以下步驟,會在後續章節詳細介紹:
- Address and Storage Allocation
- Symbol Resolution
- Relocation
Reloaction 簡單例子:
1
mov1 $0x2a, var
上述指令相當於
var=42,假設var定義在其他 object file 中,那這段指令實際上編譯完的機器碼:1
2mov 指令碼 var 42
C7 05 00 00 00 00 2a 00 00 00可以看到中間的目標地址為 0,等待 linker 修正為正確的地址。
- Relocation Entry: 被修正處
- Relocation: 地址修改的過程
Things to Remember
- Build
- Preprocess
- Compile
- Lexical analysis
- Syntax analysis
- Semantic analysis
- Intermediate code generation and optimization
- Target code generation and optimization
- Assemble
- Link
- To be continued…